Using Hermes
Hermes is an open-source JavaScript engine optimized for React Native. For many apps, using Hermes will result in improved start-up time, decreased memory usage, and smaller app size when compared to JavaScriptCore. Hermes is used by default by React Native and no additional configuration is required to enable it.
Bundled Hermes
React Native comes with a bundled version of Hermes. We will be building a version of Hermes for you whenever we release a new version of React Native. This will make sure you're consuming a version of Hermes which is fully compatible with the version of React Native you're using.
Historically, we had problems with matching versions of Hermes with versions of React Native. This fully eliminates this problem, and offers users a JS engine that is compatible with the specific React Native version.
This change is fully transparent to users of React Native. You can still disable Hermes using the command described in this page. You can read more about the technical implementation on this page.
Confirming Hermes is in use
If you've recently created a new app from scratch, you should see if Hermes is enabled in the welcome view:
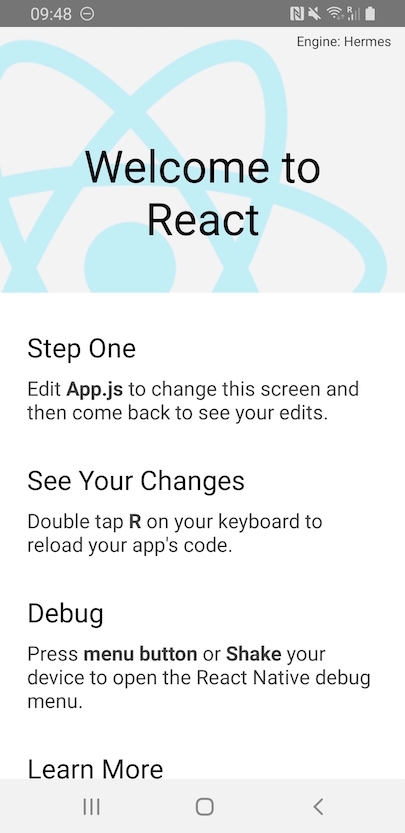
A HermesInternal global variable will be available in JavaScript that can be used to verify that Hermes is in use:
const isHermes = () => !!global.HermesInternal;
If you are using a non-standard way of loading the JS bundle, it is possible that the HermesInternal variable is available but you aren't using the highly optimised pre-compiled bytecode.
Confirm that you are using the .hbc file and also benchmark the before/after as detailed below.
To see the benefits of Hermes, try making a release build/deployment of your app to compare. For example; from the root of your project:
- Android
- iOS
- npm
- Yarn
npm run android -- --mode="release"
yarn android --mode release
- npm
- Yarn
npm run ios -- --mode="Release"
yarn ios --mode Release
This will compile JavaScript to bytecode during build time which will improve your app's startup speed on device.
Debugging JS on Hermes using Google Chrome's DevTools
Hermes supports the Chrome debugger by implementing the Chrome inspector protocol. This means Chrome's tools can be used to directly debug JavaScript running on Hermes, on an emulator or on a real, physical, device.
Note that this is very different with the "Remote JS Debugging" from the In-App Dev Menu documented in the Debugging section, which actually runs the JS code on Chrome's V8 on your development machine (laptop or desktop).
Chrome connects to Hermes running on device via Metro, so you'll need to know where Metro is listening. Typically this will be on localhost:8081, but this is configurable. When running yarn start the address is written to stdout on startup.
Once you know where the Metro server is listening, you can connect with Chrome using the following steps:
-
Navigate to
chrome://inspectin a Chrome browser instance. -
Use the
Configure...button to add the Metro server address (typicallylocalhost:8081as described above).
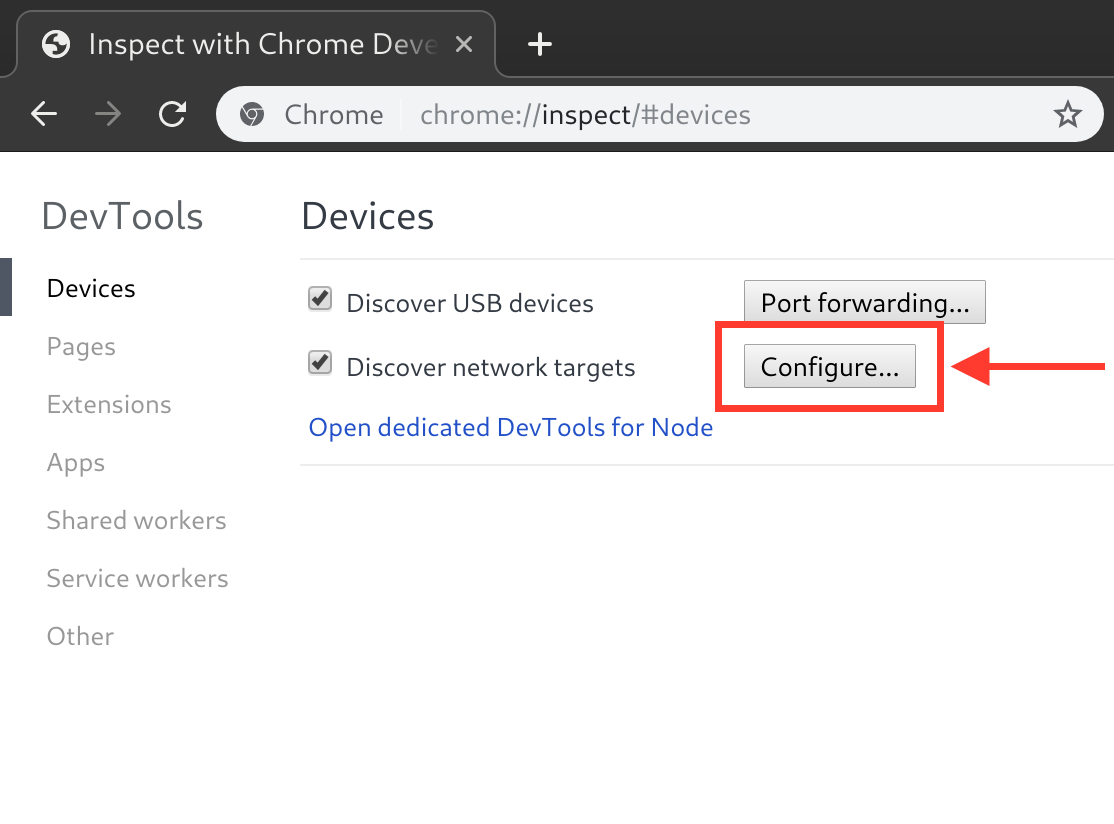
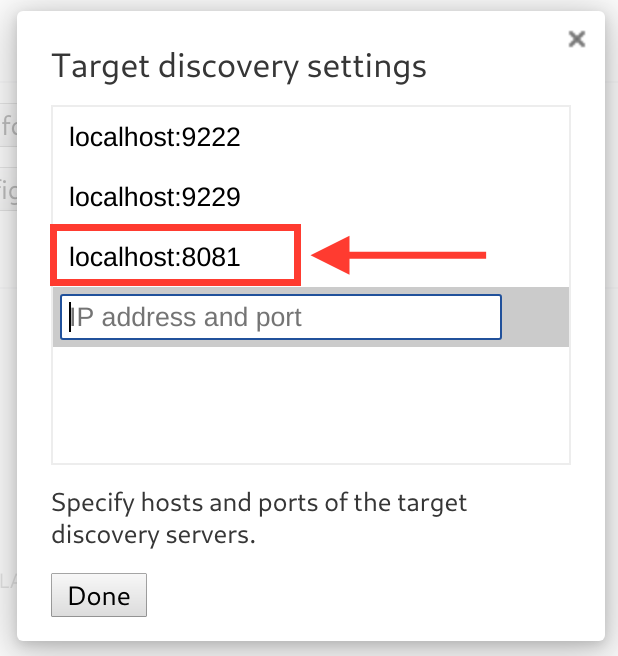
-
You should now see a "Hermes React Native" target with an "inspect" link which can be used to bring up debugger. If you don't see the "inspect" link, make sure the Metro server is running.
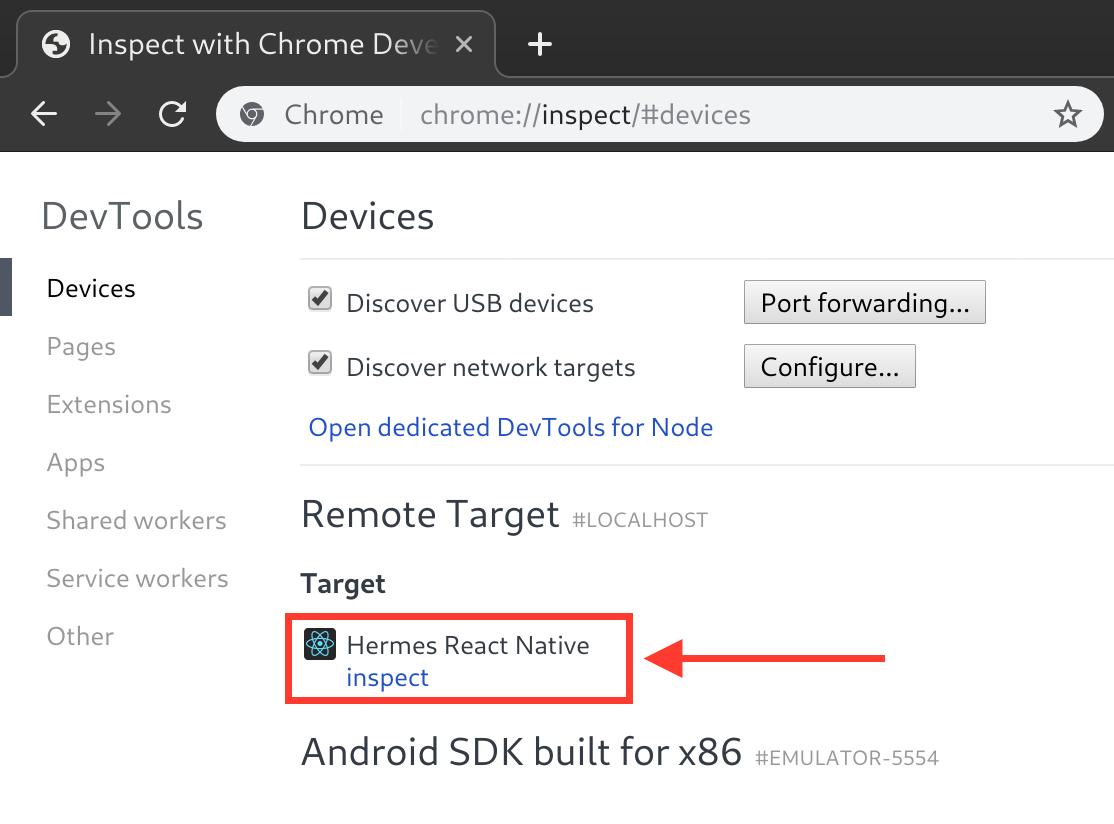
-
You can now use the Chrome debug tools. For example, to breakpoint the next time some JavaScript is run, click on the pause button and trigger an action in your app which would cause JavaScript to execute.
Enabling Hermes on Older Versions of React Native
Hermes is the default engine as of React Native 0.70. This section explains how to enable Hermes on older versions of React Native. First, ensure you're using at least version 0.60.4 of React Native to enable Hermes on Android or 0.64 of React Native to enable Hermes on iOS.
If you have an existing app based on an earlier version of React Native, you will have to upgrade it first. See Upgrading to new React Native Versions for how to do this. After upgrading the app, make sure everything works before trying to switch to Hermes.
Each Hermes release is aimed at a specific RN version. The rule of thumb is to always follow Hermes releases strictly. Version mismatch can result in instant crash of your apps in the worst case scenario.
Hermes requires Microsoft Visual C++ 2015 Redistributable.
Android
Edit your android/gradle.properties file and make sure hermesEnabled is true:
# Use this property to enable or disable the Hermes JS engine.
# If set to false, you will be using JSC instead.
hermesEnabled=true
This property was added in React Native 0.71. If you can't find it in your gradle.properties file, please refer to the documentation for the corresponding React Native version you're using.
Also, if you're using ProGuard, you will need to add these rules in proguard-rules.pro :
-keep class com.facebook.hermes.unicode.** { *; }
-keep class com.facebook.jni.** { *; }
Next, if you've already built your app at least once, clean the build:
$ cd android && ./gradlew clean
That's it! You should now be able to develop and deploy your app as usual:
- npm
- Yarn
npm run android
yarn android
iOS
Since React Native 0.64, Hermes also runs on iOS. To enable Hermes for iOS, edit your ios/Podfile file and make the change illustrated below:
use_react_native!(
:path => config[:reactNativePath],
# to enable hermes on iOS, change `false` to `true` and then install pods
# By default, Hermes is disabled on Old Architecture, and enabled on New Architecture.
# You can enable/disable it manually by replacing `flags[:hermes_enabled]` with `true` or `false`.
- :hermes_enabled => flags[:hermes_enabled],
+ :hermes_enabled => true
)
By default, you will be using Hermes if you're on the New Architecture. By specifying a value such
as true or false you can enable/disable Hermes as you wish.
Once you've configured it, you can install the Hermes pods with:
$ cd ios && pod install
That's it! You should now be able to develop and deploy your app as usual:
- npm
- Yarn
npm run ios
yarn ios
Switching back to JavaScriptCore
React Native also supports using JavaScriptCore as the JavaScript engine. Follow these instructions to opt-out of Hermes.
Android
Edit your android/gradle.properties file and flip hermesEnabled back to false:
# Use this property to enable or disable the Hermes JS engine.
# If set to false, you will be using JSC instead.
hermesEnabled=false
iOS
Edit your ios/Podfile file and make the change illustrated below:
use_react_native!(
:path => config[:reactNativePath],
# Hermes is now enabled by default. Disable by setting this flag to false.
# Upcoming versions of React Native may rely on get_default_flags(), but
# we make it explicit here to aid in the React Native upgrade process.
- :hermes_enabled => flags[:hermes_enabled],
+ :hermes_enabled => false,
)