React Native 0.83 - React 19.2, New DevTools features, no breaking changes
Today we are excited to release React Native 0.83!
This release includes React 19.2, significant new features for React Native DevTools, and support for the Web Performance and Intersection Observer APIs (Canary). This is also the first React Native release with no user facing breaking changes.
Highlights
React 19.2
This release includes React 19.2, bringing the new <Activity> and useEffectEvent APIs to React Native.
At time of release, react-native@0.83.0 depends on react@19.2.0, and you might also have seen the recent Critical Security Vulnerability in React Server Components.
We want to stress that React Native is NOT directly affected by this vulnerability, as it does not depend on the impacted packages:
react-server-dom-webpackreact-server-dom-parcelreact-server-dom-turbopack
However, if you are using React Native as part of a monorepo where these packages may be present, please check and upgrade them immediately.
We will update all React dependencies to 19.2.1 in our next patch release.
<Activity>
<Activity> lets you break your app into "activities" that can be controlled and prioritized. You can use Activity as an alternative to conditionally rendering parts of your app, and it currently supports 2 modes: 'visible' and 'hidden'.
hidden: hides the children, unmounts effects, and defers all updates until React has nothing left to work on.visible: shows the children, mounts effects, and allows updates to be processed normally.
One interesting feature of trees hidden using <Activity mode='hidden'> is that they preserve their state. So, when they become visible again, they, for example, keep the search status and the selection from a previous user interaction.
| React 19.1.1 | React 19.2.1 |
|---|---|
 |  |
You can read more about <Activity> in the React docs.
useEffectEvent
One common pattern with useEffect is to notify the app code about some kind of "event" from an external system. The problem with this approach is that a change to any value used inside such an event will cause the surrounding Effect to re-run.
To solve this, most users disable the lint rule and exclude the dependency. But that can lead to bugs since the linter can no longer help you keep the dependencies up to date if you need to update the Effect later.
With useEffectEvent, you can split the "event" part of this logic out of the Effect that emits it.
You can read more about useEffectEvent in the React docs.
New DevTools features
In 0.83 we're excited to deliver some long awaited features and quality of life improvements to React Native DevTools.
Network and Performance panels
Network inspection and performance tracing are two powerful new capabilities in React Native DevTools, available today.
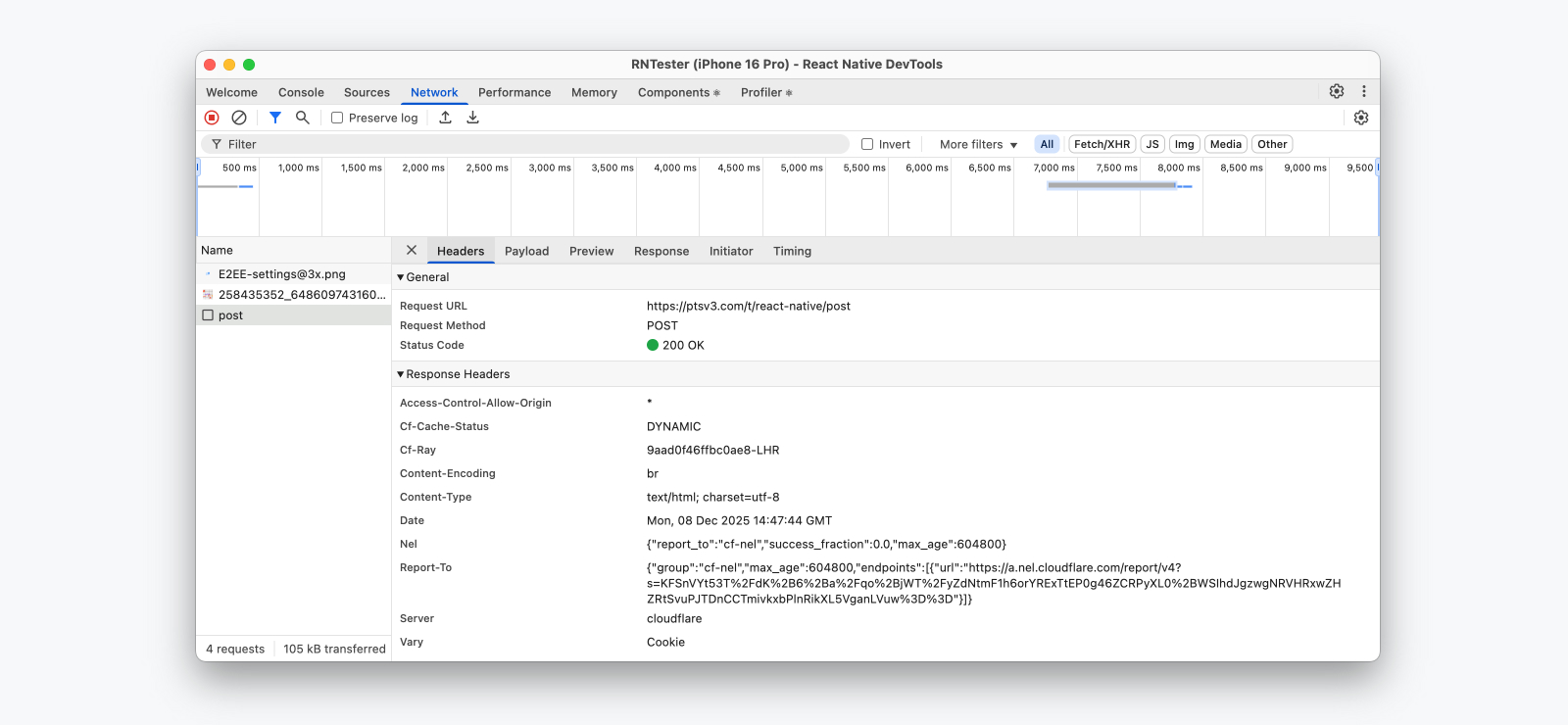
Network inspection, now available for all React Native apps, allows you to view and understand the network requests made by your app. Logged requests provide detailed metadata such as timings and headers sent/received, as well as response previews. And — for the first time — you can use the Initiator tab to see where in your code a network request originated.
💡 Network event coverage, Expo support
Which network events are captured?
Today, we record all network calls through fetch(), XMLHttpRequest, and <Image> — with support for custom networking libraries, such as Expo Fetch, coming later.
Expo Network differences
Because of this, apps using Expo will continue to see the "Expo Network" panel — a separate implementation by the Expo framework which will log these additional request sources but has slightly reduced features.
- Coverage for Expo-specific network events.
- No request initiator support.
- No Performance panel integration.
We're working with Expo to integrate Expo Fetch and third party networking libraries with our new Network inspection pipeline in future releases.
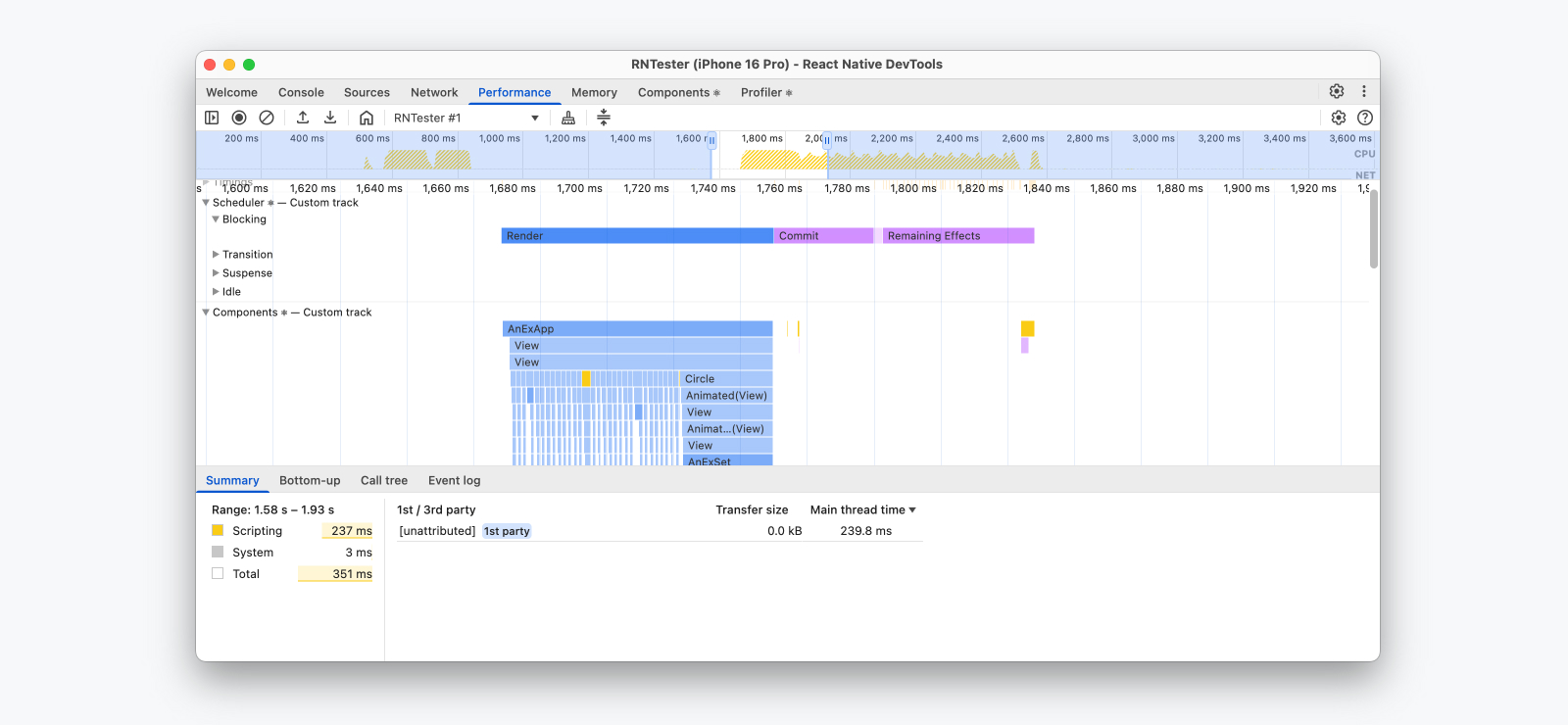
Performance tracing allows you to record a performance session within your app to understand how your JavaScript code is running and what operations took the most time. In React Native, we show JavaScript execution, React Performance tracks, Network events, and custom User Timings, rendered in a single performance timeline.
Together with support for the Web Performance APIs in 0.83, this is a powerful feature set providing fine-grained visibility into what might be making your React Native apps slow. We encourage everyone to try out the Performance panel and make it a part of your daily workflow.
Learn more about our newest React Native DevTools features and React Performance tracks.
New desktop app
Previously, React Native DevTools launched in a browser window and required Chrome or Edge to be installed. Today, we're introducing a vastly improved desktop experience with our new bundled desktop app. It features:
- The same zero-install setup as before, now with no web browser requirement.
- Faster launch via a lightweight and notarized desktop binary. In rare cases where this cannot be downloaded (such as a corporate firewall), we fall back to the previous browser launch flow.
- Better windowing, with improved multitasking on macOS, auto-raise on breakpoint, auto-raise when reconnecting to the same app, and saved window arrangements on relaunch.
- Improved reliability by running DevTools separately from your personal browser profile. In particular, this resolves bug reports we have received about certain preinstalled Chrome extensions causing React Native DevTools to break.

Intersection Observers (Canary)
As part of our effort to bring web APIs to React Native, we have added support for IntersectionObserver in the canary release for 0.83.
IntersectionObserver allows you to asynchronously observe layout intersections between a target element and its ancestor. Please see our API and implementation docs for more details. We've also included examples in RNTester.
Other changes
Web Performance APIs as stable
As introduced in 0.82, React Native now implements a subset of the Performance APIs available on Web — now rolled out as stable:
- High Resolution Time: defines
performance.now()andperformance.timeOrigin. - Performance Timeline: defines
PerformanceObserverand methods to access performance entries in the performance object (getEntries(),getEntriesByType(),getEntriesByName()). - User Timing: defines
performance.markandperformance.measure. - Event Timing API: defines
evententry types reported toPerformanceObserver. - Long Tasks API: defines
longtaskentry types reported toPerformanceObserver.
These APIs allow tracking different aspects of performance in your app, visible in the Performance panel in React Native DevTools, as well as at runtime via PerformanceObserver.
PerformanceObserver also works in production builds, opening new opportunities for capturing real world performance metrics in your apps.
Experimental - Hermes V1

Hermes V1 is the next evolution of Hermes, with improvements in the compiler and the VM that significantly boost JavaScript performance.
In React Native 0.82, we released Hermes V1 as an experimental opt-in. And in 0.83, Hermes V1 includes further performance improvements.
💡 Enabling Hermes V1
Note: While Hermes V1 is in the experimental phase, you’ll need to build React Native from source to try it out.
To try Hermes V1 in your own project, use the following steps:
- Force your package manager to resolve the experimental version of Hermes V1 compiler package by modifying the corresponding section of your package.json file (note that the current versioning convention is only for the experimental phase of Hermes V1):
- yarn
- npm
"resolutions": { "hermes-compiler": "250829098.0.4" }
"overrides": { "hermes-compiler": "250829098.0.4" }
-
Enable Hermes V1 for Android by adding hermesV1Enabled=true inside
android/gradle.properties:android/gradle.propertieshermesV1Enabled=trueAlso, configure React Native to build from source by editing android/settings.gradle:
android/settings.gradleincludeBuild('../node_modules/react-native') {
dependencySubstitution {
substitute(module("com.facebook.react:react-android")).using(project(":packages:react-native:ReactAndroid"))
substitute(module("com.facebook.react:react-native")).using(project(":packages:react-native:ReactAndroid"))
substitute(project(":packages:react-native:ReactAndroid:hermes-engine")).using(module("com.facebook.hermes:hermes-android:250829098.0.1"))
}
} -
Enable Hermes V1 for iOS by installing pods with
RCT_HERMES_V1_ENABLED=1environment variable.RCT_HERMES_V1_ENABLED=1 bundle exec pod installKeep in mind that Hermes V1 is not compatible with the precompiled React Native builds, so make sure you don’t use the
RCT_USE_PREBUILT_RNCOREflag when installing pods. -
To confirm if your app is running Hermes V1, execute the following code within your app or the DevTools console. This code will return the Hermes version, which should match the version specified in step 1 (250829098.0.1):
// expecting "250829098.0.1" in Hermes V1
HermesInternal.getRuntimeProperties()['OSS Release Version'];
Experimental - Compile out the Legacy Architecture on iOS
In this release, we are adding a new flag for iOS that allows you to compile out the Legacy Architecture from the codebase. If your app is already on the New Architecture, you can try to remove the legacy architecture code by installing your pods with:
RCT_REMOVE_LEGACY_ARCH=1 bundle exec pod install
This should reduce both the build time and the size of your app. The improvements depend on how many third party libraries you are using: in our tests, using a new app without dependencies, the build time was reduced from 73.0 seconds to 58.2 seconds, and the app size went from 51.2 Mb to 48.2 Mb.
RCT_REMOVE_LEGACY_ARCH is not compatible with React Native precompiled binaries. If you are using precompiled binaries, you'll need to reinstall the pods and build the app from source.
Experimental - Debug your precompiled binaries on iOS
In this release, we've implemented the ability to debug the React Native code that is shipped with a precompiled binary. This is primarily helpful to library maintainers or if you are developing a native module or a native component.
To debug the binary code shipped with the React Native precompiled binary, follow these steps:
# From the ios folder of your project
bundle exec pod cache clean --all
bundle exec pod deintegrate
RCT_USE_RN_DEP=1 RCT_USE_PREBUILT_RNCORE=1
RCT_SYMBOLICATE_PREBUILT_FRAMEWORKS=1 bundle exec pod install
open <your-project>.xcworkspace
The magic is done by the RCT_SYMBOLICATE_PREBUILT_FRAMEWORKS flag, which instructs CocoaPods to download the React Native dSYM files and expand them in the proper folder.
At this point, you can put a breakpoint in your app, for example in AppDelegate.swift, and build and run the app from Xcode.
When the application pauses, open the Xcode console and run the LLDB command:
# If you are running the app in the simulator
add-dsym <path-to-your-app>/ios/Pods/React-Core-prebuilt/React.xcframework/ios-arm64_x86_64-simulator/React.framework/dSYMs/React.framework.dSYM
# If you are running the app on a physical device
add-dsym <path-to-your-app>/ios/Pods/React-Core-prebuilt/React.xcframework/ios-arm64/React.framework/dSYMs/React.framework.dSYM
Now you can step into the React Native code.
Breaking Changes
We're working hard to make React Native releases more predictable and easier to upgrade. React Native 0.83 is the first release with no user facing breaking changes.
If you are on React Native 0.82, you should be able to upgrade your app to React Native 0.83 without any changes to your app code.
To learn more about what we consider a breaking change, have a look at this article.
Deprecations
This release ships two deprecations that are Android specific:
- Networking: The
sendRequestInternalmethod is being phased out and it is now deprecated. - Animation:
startOperationBatchandfinishOperationBatchare now deprecated.
Acknowledgements
React Native 0.83 contains over 594 commits from 56 contributors. Thanks for all your hard work!
We want to send a special thank you to those community members that shipped significant contributions in this release:
- Ruslan Lesiutin, Moti Zilberman, and Alex Hunt for the React Native DevTools Performance and Network features.
- Moti Zilberman for the React Native DevTools desktop app.
- Luna Wei for Intersection Observers.
- Rubén Norte for the Web Performance APIs.
- Dawid Małecki and Jakub Piasecki for the rollout of Hermes V1.
- Ramanpreet Nara for the
RCT_REMOVE_LEGACY_ARCHflag. - Christian Falch for precompiled iOS binary debugging.
Upgrade to 0.83
Please use the React Native Upgrade Helper to view code changes between React Native versions for existing projects, in addition to the Upgrading docs.
To create a new project:
npx @react-native-community/cli@latest init MyProject --version latest
If you use Expo, React Native 0.83 will be available in SDK 55, which will be released in January 2026.
Supported versions
0.83 is now the latest stable version of React Native and 0.80.x moves to unsupported. For more information see React Native's support policy.



